To make sure your webpage loads and appears fast for your users, load only the CSS and JS code that your page requires to appear correctly. If some of your CSS or JS code is only needed later, when the user starts interacting with the webpage, then consider deferring this code until it's really needed.
In Chromium-based browsers #
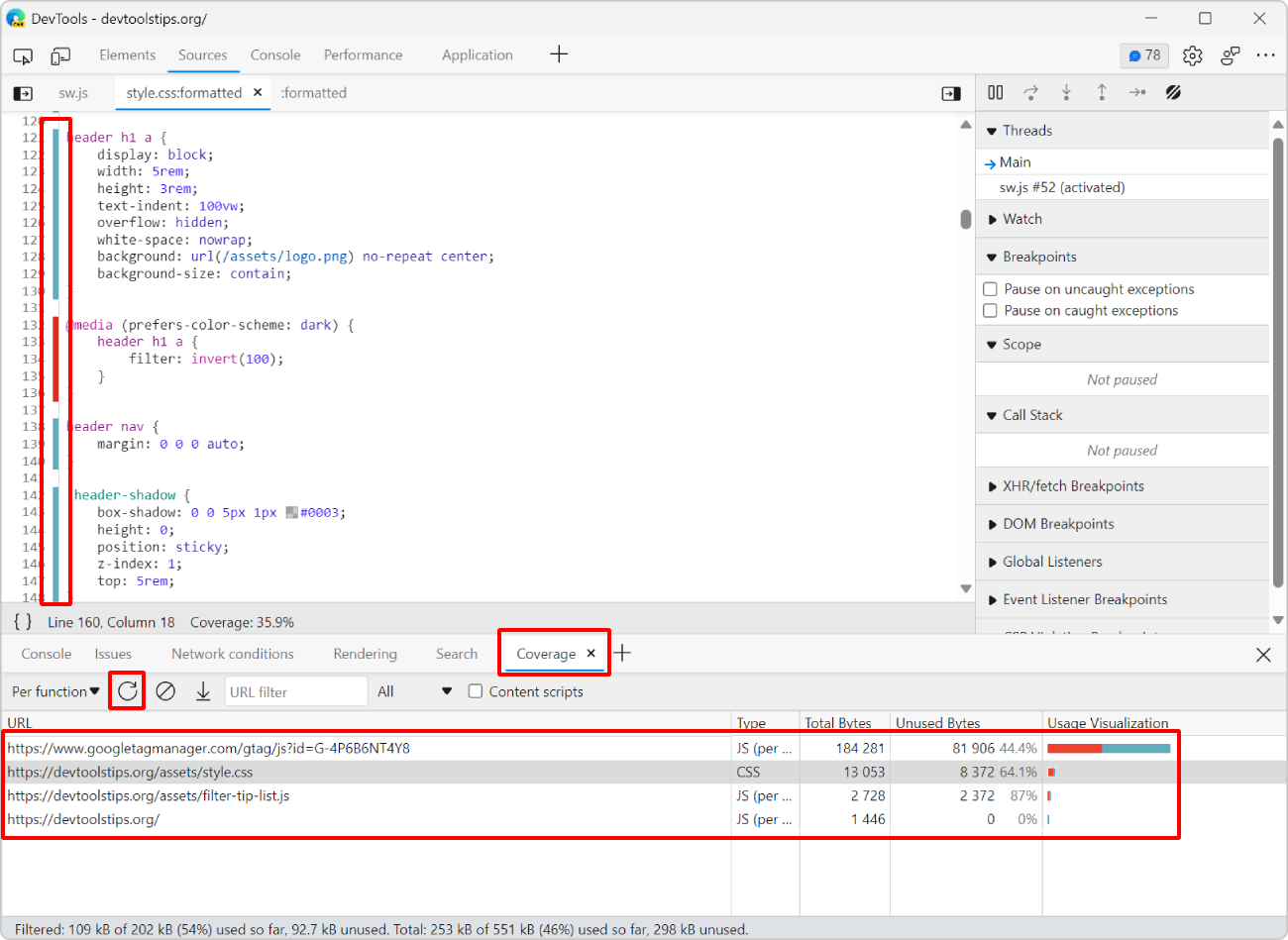
Chrome and Edge have a useful Coverage tool that can help identify which parts of code are unused. To detect unused code on page load:
-
Open the Coverage tool by using the Command Menu: type Ctrl+Shift+P (or cmd+Shift+P on mac), then type Coverage and press Enter.
-
In Coverage, click the Start instrumenting coverage and refresh the page button (i.e., the refresh button).
-
Wait for the webpage to reload and for the coverage report to appear.
The report shows a list of CSS and JS files with a percentage of unused bytes.
-
Click on any of the files to open it in the Sources tool.
The file appears in the tool, and the line number gutter on the left indicates which lines were used, in blue, and which were unused, in red.
You can now decide whether some parts of your code can be loaded later, when needed only.
In Safari #
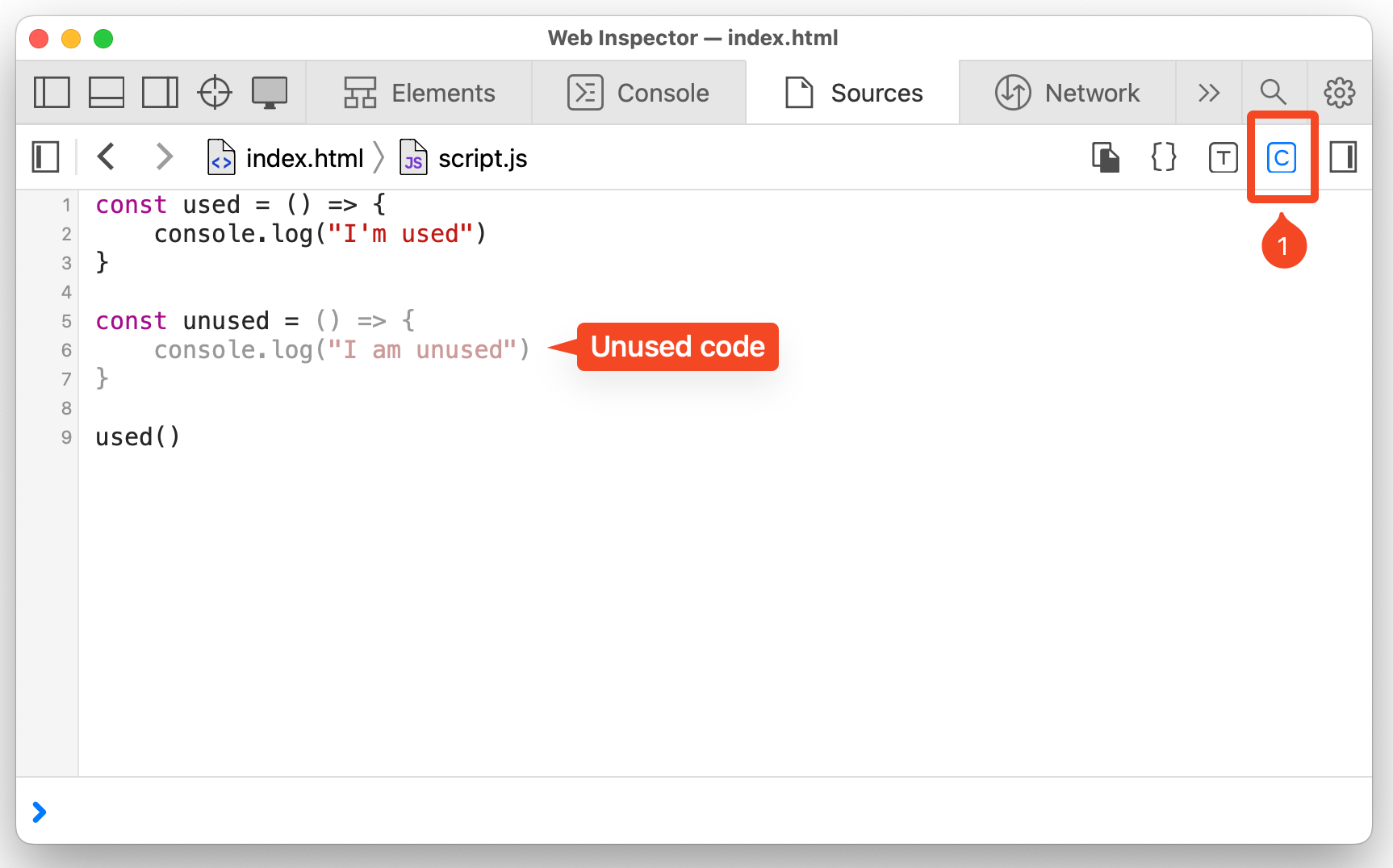
In Safari, you can detect unused JS code, with the following steps,
-
In the Sources panel, open the JS file from the left sidebar.
-
Click the coverage icon
Cin the toolbar (top-right) to start detecting unexecuted code. -
Refresh the page.
-
Lines of code that are not executed on page load are greyed out. Executed lines are displayed as normal.