The accessibility tree is a representation of the structure of a web page that is used by assistive technologies such as screen readers. It is similar to the DOM tree, but it only includes the elements that are relevant for accessibility. For example, it includes text nodes, links, images, or form controls, but not generic elements such as <div> or <span>.
It's best to actually use a screen reader, or another assistive technology, to experience how your webpage is perceived by users with disabilities. But, it can sometimes be useful to see the accessibility tree in DevTools to understand how a page is structured.
Firefox #
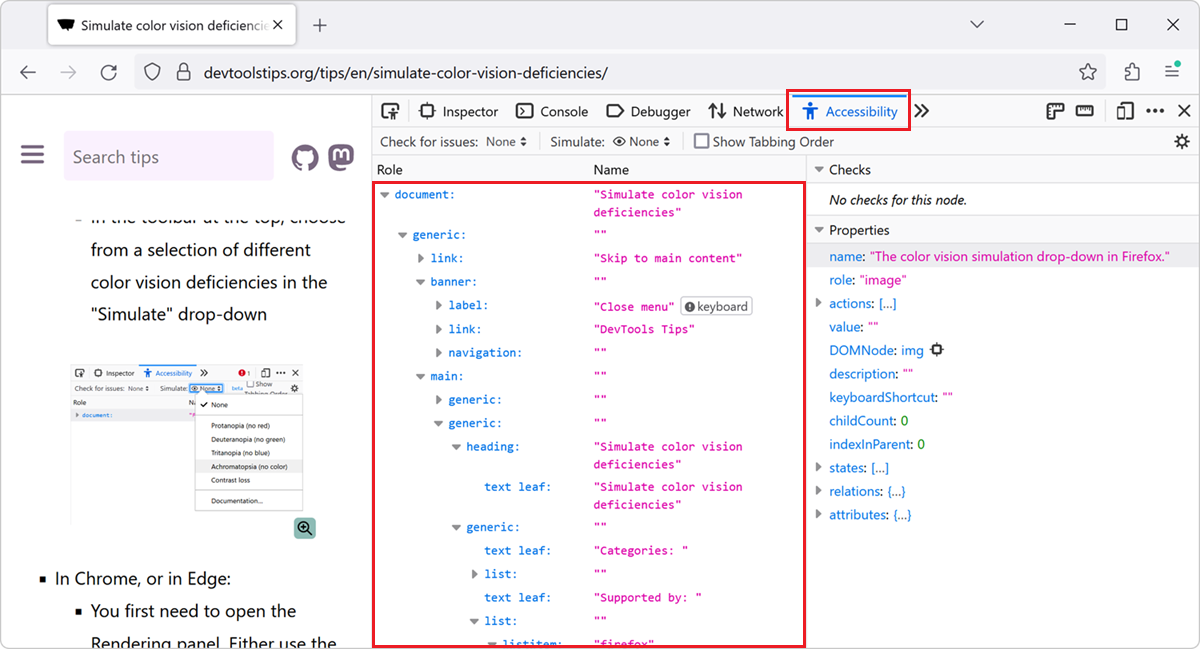
Firefox has a dedicated Accessibility tool. To open it:
- Press F12 to open DevTools.
- In the main toolbar, click the Accessibility tab.
- Expand the document node that's displayed in the tool to reveal the accessibility tree.
Supported features include:
- Hovering over nodes in the tree highlights the corresponding DOM elements in the page.
- Selecting nodes reveals their accessibility properties in the sidebar.
- Accessibility issues are displayed next to the corresponding nodes in the tree.
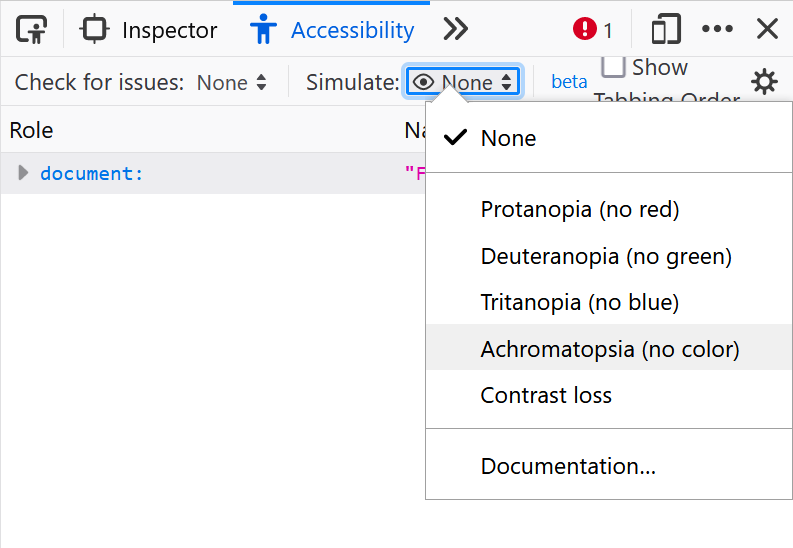
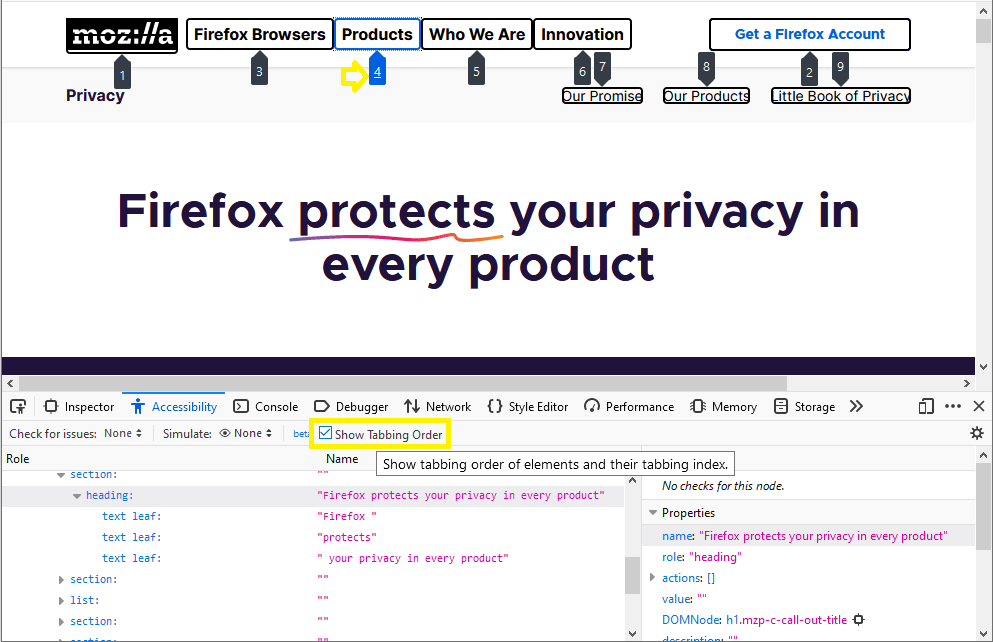
- Checking for more issues, tabbing order, or simulating color vision deficiencies from the toolbar.
Chrome and Edge #
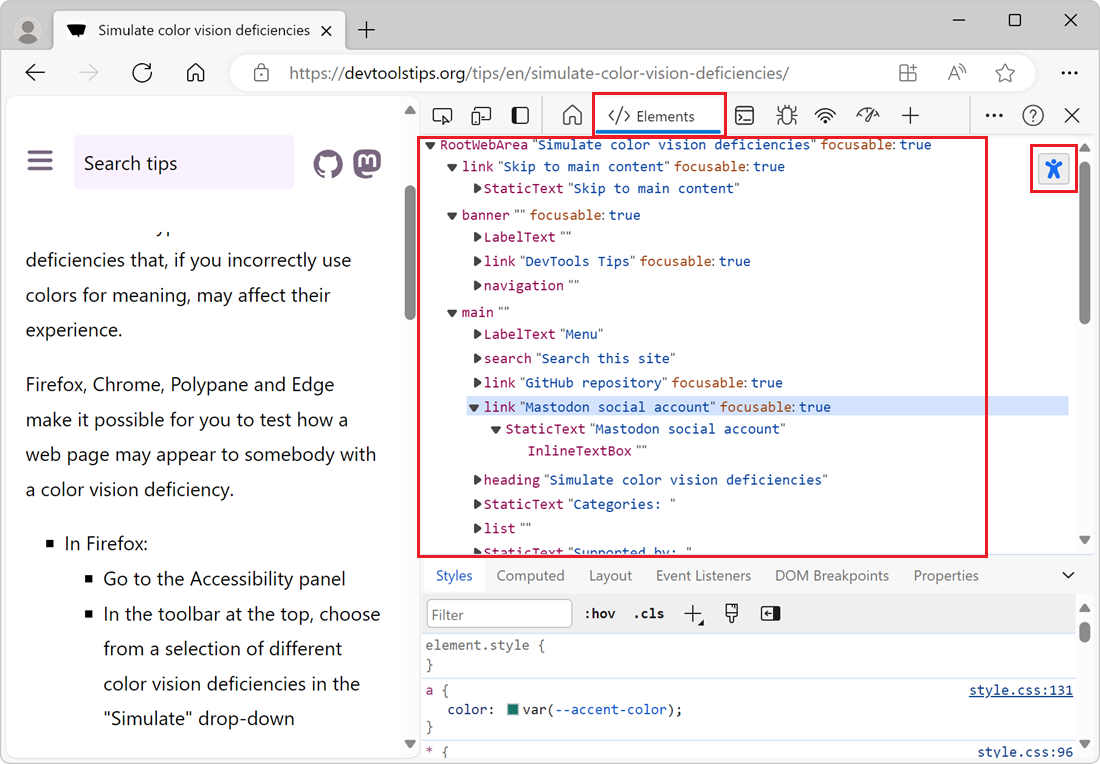
Chrome and Edge have an option to display the accessibility tree in the Elements tool, instead of the DOM tree. To enable it:
- Press F12 to open DevTools.
- Go to the Settings panel by pressing F1.
- In the sidebar, click Experiments.
- Find the Enable full accessibility tree view in the Elements panel checkbox and select it.
- Restart DevTools.
To see the accessibility tree in the Elements tool:
- Open the Elements tool.
- Click Switch to Accessibility Tree View in the top-right corner of the DOM tree.
Supported features include:
- Hovering over nodes in the tree highlights the corresponding DOM elements in the page.
- Selecting nodes reveals the matching CSS styles in the Styles pane and lets you update them.